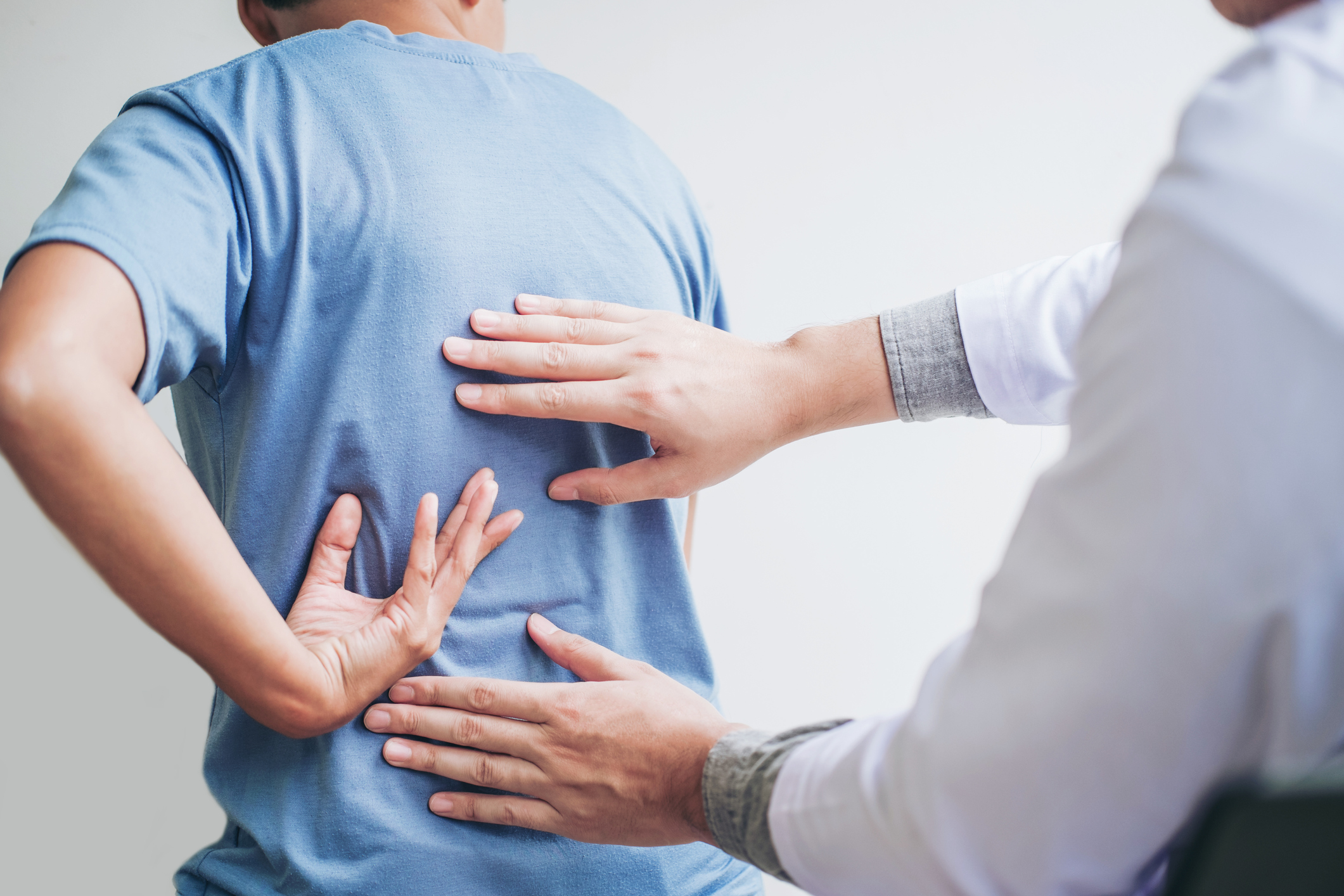
Arthritis of the spine can lead to joint changes causing pain and inflammation. Damage to the facet joints can occur anywhere along the spine but is more common in the neck and low back. It usually becomes more of a problem as people age, although it can occur in younger people as the result of an injury. Arthritis may be related to wear and tear over the years, autoimmune triggers, other medical conditions such as diabetes, or obesity. Sometimes the cause is unknown. The joint damage from arthritis is not reversible.
These are common types of arthritis that affect the spine:
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is the most common type of spinal arthritis and usually develops in the low back (lumbar spine). Over time, the protective cartilage that cushions the spine breaks down between the joints. The result is inflammation, pain, and stiffness. Bone spurs that press on nerves may form. Degeneration of discs also contributes to the problem. As the discs become thinner, more pressure occurs on the facet joints which makes osteoarthritis worse.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that attacks the lining of the joints. RA is not the result of wear and tear. The immune system of a patient suffering from RA attacks the joints and damages them. It may manifest in any joints in the body including in the spine. The neck is often affected, and pain may be felt all the time, not just when the joints are being used. Women seem to be at higher risk for rheumatoid arthritis than men.
Spondyloarthritis
Spondyloarthritis – Several types of this inflammatory disease can affect the joints of the spine. Two of the most common forms are psoriatic arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis, which affects the sacroiliac joints at the bottom of the spine. In some cases, many vertebrae can actually fuse together. These disorders are due to abnormal inflammation of the involved joints.
Diagnosis of spinal arthritis generally involves a complete medical evaluation with x-rays of the affected area. A CT scan, MRI, and bone scan can help determine nerve damage. Blood tests are used to confirm whether an autoimmune disease is the cause.
Symptoms of spinal arthritis are pain, stiffness, swelling, and loss of movement or flexibility. If any nerves have been affected, there may be numbness and weakness in the legs or arms. Arthritis in the neck may cause headaches at the back of the head just above the neck.
Nonsurgical treatments focus on controlling pain and helping to restore function. These may include pharmacological pain management, the use of over the counter or prescription antiinflammatory drugs or corticosteroid drugs in the form of pills or injections. These medicines treat the inflammation and result in reduced pain. Physical therapy, or functional
rehabilitation, may help the patient improve flexibility and range of motion. Obese patients can reduce stress on their joints through weight loss. Surgical treatments may be beneficial if other treatments have not been successful. A surgeon can relieve stress on the nerve roots and spinal cord if bone spurs are pressing on them.
Recommended surgical procedures may include laminectomy, foraminotomy, or discectomy. If there is more severe damage causing weakness in the structure of the spine more extensive surgery may be necessary. The spine can be stabilized in a procedure called spinal fusion. A complete evaluation of the patient’s symptoms and their diagnosis will determine whether surgery is an appropriate option.