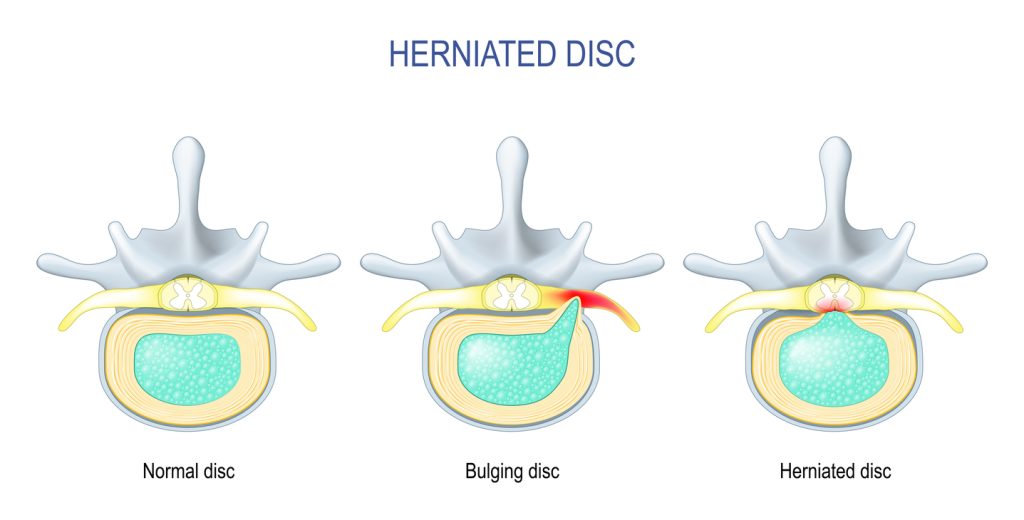
A disc herniation is a problem with one of the rubber-like pads between each spinal vertebrae. The discs act as shock absorbers and provide support and stability for the spine. Discs have a tough outer membrane and a gel-like center core. A herniation means that the outer membrane has cracked or torn, allowing the inner gel to leak out.
Herniated discs put pressure on the spinal canal or nerve roots. The leaking gel can cause irritation and pain to the surrounding nerves. The most common site of disc herniation is the lumbar spine (lower back). Most lumbar herniations occur between the L4-L5 level and the L5-S1 level.
What causes lumbar discs to herniate?
A disc herniation may result from a single accident or injury, such as improper lifting or twisting the back while lifting. Herniations may occur because of repetitive activities that put stress on the low back. Aging is an added risk factor, since discs dry out and lose resiliency as we get older. Genetics also plays a role. Obesity, poor posture, and an inactive lifestyle contribute to the chance of disc herniation.
Symptoms of a Herniated Disc
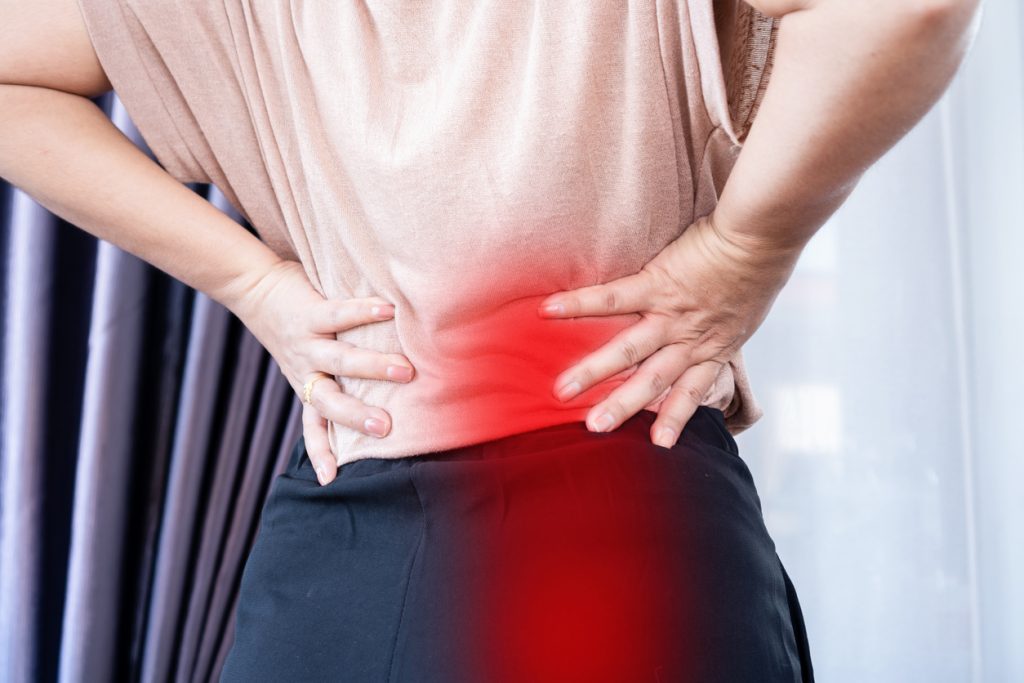
Symptoms of lumbar disc herniation include:
- Dull or sharp pain in the low back. Certain movements such as bending forward, coughing, sneezing, and laughing can intensify the pain. Prolonged sitting or standing may worsen pain.
- Sciatica – Burning, tingling, pain, and numbness extending from the buttocks down the leg or into the foot. Usually one leg is affected.
- Muscle spasms or leg cramps
- Leg weakness, which may include foot drop
Do herniated discs require surgery?
Most lumbar disc herniations do not require surgery, although some cases may take four to six months to resolve. Many nonsurgical treatments are effective in relieving pain and promoting healing. Conservative treatments may include muscle relaxers to help with spasms, anti-inflammatory medications to relieve pain and swelling, and occasionally stronger prescription pain medications. Heat and cold therapy can be helpful. Physical therapy may be recommended, along with stretching and strengthening exercises to relieve pain and increase flexibility. Patients with severe pain may benefit from epidural injections for pain management.
If conservative treatments are not effective, surgery to remove the damaged disc may be recommended. These procedures can often be performed using minimally invasive surgical techniques.
Atlanta Brain and Spine Care
Our neurosurgeons offer patients access to some of the world’s most advanced treatments and procedures in five convenient metro locations. Contact us to schedule a consultation with one of our spine specialists.